Understanding Selenium Locators for Effective Web Element Identification
Web test automation relies heavily on accurately locating and interacting with elements on a webpage. Selenium, the industry-standard automation framework, offers various powerful locator strategies to identify web elements efficiently. This guide explores the most effective locator methods with practical Java examples.
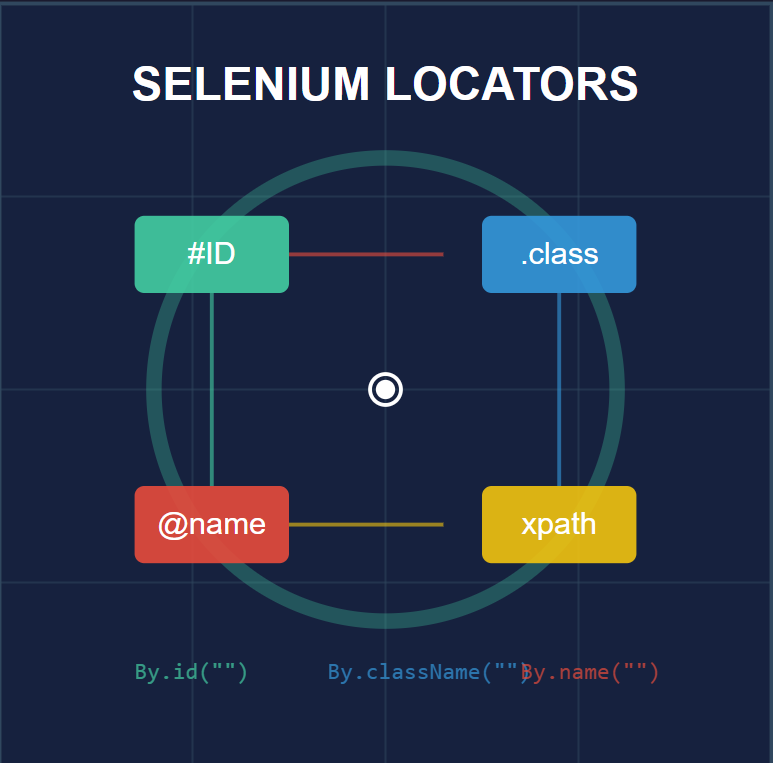
There are 8 types of locators in selenium, which are mentioned below
Please refer this URL for HTML page, all the locator values are extracted from below page
Page Link: https://automationtestershub.com/locator-examplepage/
1. ID Locator: The Most Reliable Method
The ID locator is the fastest and most reliable way to locate elements, as IDs are unique within a webpage.
// Finding element by ID
WebElement loginButton = driver.findElement(By.id("login-button"));
WebElement usernameField = driver.findElement(By.id("user_email"));
Best Practices for ID Locators:
- Always prioritize ID locators when available
- Ensure IDs are unique and static
- Avoid dynamic IDs that change on page refresh
2. CSS Selectors: Versatile and Powerful
CSS selectors offer flexibility and better performance compared to XPath.
// Basic CSS selector examples
WebElement submitButton = driver.findElement(By.cssSelector(".submit-btn"));
WebElement headerTitle = driver.findElement(By.cssSelector("h1.main-title"));
// Advanced CSS selector combinations
WebElement nestedElement = driver.findElement(By.cssSelector("div.container > form#login > input[type='text']"));
CSS Selector Tips:
- Use class combinations for better precision
- Leverage parent-child relationships
- Utilize attribute selectors for specific matching
3. XPath: Navigate Complex DOM Structures
While slightly slower than CSS selectors, XPath provides powerful navigation capabilities.
// Absolute XPath (avoid when possible)
WebElement logo = driver.findElement(By.xpath("/html/body/div[1]/header/img"));
// Relative XPath (preferred approach)
WebElement searchBox = driver.findElement(By.xpath("//input[@placeholder='Search']"));
// Contains and text-based XPath
WebElement dynamicElement = driver.findElement(By.xpath("//div[contains(@class, 'user-profile')]"));
WebElement linkText = driver.findElement(By.xpath("//a[contains(text(), 'Sign Up')]"));
<pre>
XPath Best Practices:
- Prefer relative XPath over absolute paths
- Use contains() for dynamic attributes
- Combine multiple attributes for accuracy
4. Name Locator: Simple but Effective
Name locators work well for form elements but may not be unique.
// Using name attribute
WebElement passwordField = driver.findElement(By.name("password"));
WebElement rememberMe = driver.findElement(By.name("remember_me"));
5. Class Name: Group-based Selection
Class names are useful for finding multiple similar elements.
// Finding elements by class name
List<WebElement> menuItems = driver.findElements(By.className("nav-item"));
WebElement firstButton = driver.findElement(By.className("btn-primary"));
6. Dynamic Element Location Strategies
Modern web applications often have dynamic content. Here’s how to handle them:
// Wait for element to be visible
WebDriverWait wait = new WebDriverWait(driver, Duration.ofSeconds(10));
WebElement dynamicContent = wait.until(ExpectedConditions.visibilityOfElementLocated(
By.cssSelector(".dynamic-content")
));
// Custom wait conditions
WebElement element = wait.until(driver -> {
try {
return driver.findElement(By.id("loading-complete"));
} catch (NoSuchElementException e) {
return null;
}
});
Advanced Techniques and Combinations
1. Chaining Locators
// Find element within another element
WebElement form = driver.findElement(By.id("login-form"));
WebElement emailInput = form.findElement(By.cssSelector("input[type='email']"));
2. Custom Attribute Locators
// Using custom data attributes
WebElement customElement = driver.findElement(By.cssSelector("[data-testid='submit-button']"));
WebElement customAttr = driver.findElement(By.xpath("//*[@data-custom='special']"));
Best Practices for Reliable Element Location
- Prioritize Locator Types:
- ID > CSS Selector > XPath > Other methods
- Create Robust Selectors:
- Use unique and stable attributes
- Avoid relying on index-based selection
- Implement explicit waits for dynamic content
- Maintain Locator Repository:
public class LoginPageLocators {
public static final By USERNAME_FIELD = By.id("username");
public static final By PASSWORD_FIELD = By.id("password");
public static final By LOGIN_BUTTON = By.cssSelector(".login-btn");
// Page Object Model implementation
public void login(String username, String password) {
driver.findElement(USERNAME_FIELD).sendKeys(username);
driver.findElement(PASSWORD_FIELD).sendKeys(password);
driver.findElement(LOGIN_BUTTON).click();
}
}
Hope you understood the locators, we will be covering Xpath and CSS selectors in depth in upcoming articles, stay tuned